Experts divided the evolution of the internet into three very distinct phases. And currently, we are at the gateway between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, where both exist together, but moving forward, Web3 will be the prominent version of the World Wide Web.
What is Web3?
Web3 is a decentralized web powered by peer-to-peer servers on the blockchain. It includes features like semantic web, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality, and serves as the foundation for cryptocurrency, NFTs, and other decentralized applications (dApps).
Unlike Web2 which runs servers on multiple centralized servers, Web3 instead runs on blockchain networks. To further understand Web3 and how it came to be, we need to have a better understanding of both Web1 and Web2.
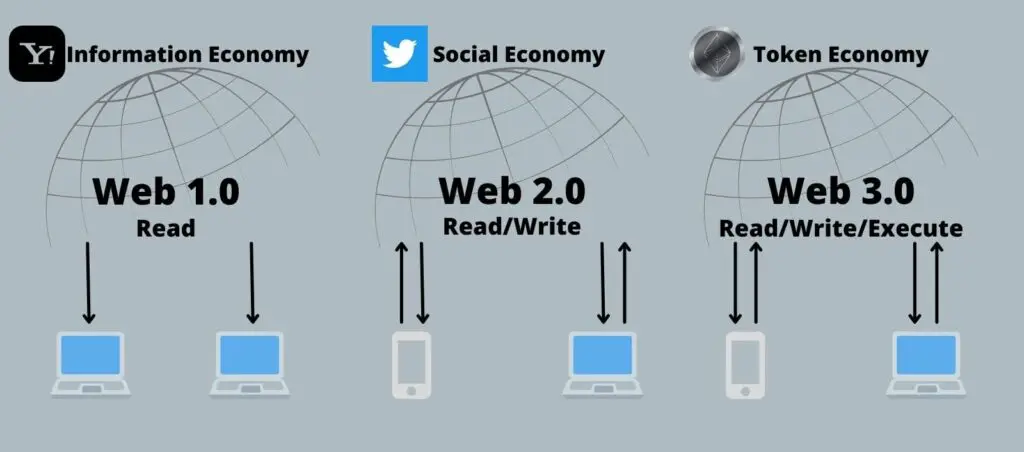
Web 1.0 (1989 – 2005)
Web 1.0, aka the static web, is referred to as the first iteration of the web. It is usually called the read-only phase of the internet. Where all the users were only consumers of the information provided and were unable to interact with it on a meaningful level. Web 1.0 lasted approximately from 1989 until 2005.
Web 2.0 (2005 – Present)
Web 2.0 is when the internet became more interactive and is also known as the social web. The social web allows users to create and consume various forms of content, as well as interact with it and communicate with others. It was during Web 2.0 when monetization was introduced and people began to make money from their content through ads and selling goods or services.
Examples of Web 2.0 include blog sites and social media platforms such as MySpace, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.
Web 3.0 (2014 – Present)
Web 3.0 was first introduced by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood in 2014. It refers to the latest iteration of the internet that incorporates new technologies such as the blockchain which is the foundation for NFTs, DAOs, and cryptocurrency, which has become synonymous with the term decentralization.
In essence, data and content ownership are all monopolized and centralized by a number of people as opposed to a single large corporation.
Web 3.0 promises a safer internet with less threat of malicious attacks as well as a verifiable and transparent internet that is completely immersive and gives power back to the people. In short, Web3 is a decentralized version of Web2. While Web2 runs servers on multiple centralized servers, Web3 instead runs on blockchains that are driven by peer-to-peer nodes (servers).
How Does Web3 Work?
Web3 apps are either built on blockchains, decentralized networks of numerous peer-to-peer nodes (servers), or a hybrid of the two that creates a crypto-economic protocol. These programs are commonly referred to as decentralized apps (dApps).
On the surface level, Web3 will not change much for the average user experience. Most of the functionality change will be behind the scenes. Web3 aims to be a decentralized version of Web2. Through Web3, users will be in control of their data, identity, and their digital assets, which are recorded for the public to see on the blockchain.
Building the internet on the blockchain means that there is no single entity in control of a Web3 app, these apps are identified as Decentralized Apps or dApps. The way websites and apps work today is through their servers. Information goes to the server, and it flows out of the server.
Your action online gets a response and everything happening in between is all the platform provider knows. The security protocols in place, the privacy protection measures, and other actions on data are often unknown to the user. This is one of the reasons for Web3’s existence.
The way Web3 changes this process is through blockchain, which is a digital and distributed ledger system, wherein all the participating systems act as a node. In simple words, it is a way of recording information, which uses a network of computers instead of a single computer.
This makes it very difficult, if not impossible, to hack or cheat the system. Thanks to the existence of this network of computers, Web3 does not rely on centralized servers to work.
For example, when using Web3 you are able to send a message to your friend without your messages flowing through the app’s servers. Similarly, you can send and receive money and digital assets, without a single centralized server watching your every move.
Why is Web3 so important?
Web3’s importance stems from it giving power back to the people and away from the hands of institutions. Web3 gives creators the power to own their creations and monetize them however they please. Also, creators can provide more value and trust to others through the security and transparency of blockchain technology.
Web3 is an open book, the code is open-source, governance is clear and transparent, and transactions can be verified by anyone. This of course is not to say that there is a lack of privacy.
In fact, Web3 protects privacy through encryption technology that provides and protects the privacy of everyone, which is a safer privacy system. This openness and transparency have brought unprecedented and rapid development since any innovation can be adopted by even latecomers.
In the Web3 world, there are no separating walls, communication is barrier-free, and development is of course exponentially faster.
Web 3.0 can be described with three words; verifiable, trustless, and permissionless.
Verifiable comes from the fact that Web3 is built from on the blockchain which is created by an open and accessible community of developers, and verifiable by anyone using Web3.
Trustless isn’t a negative word in this situation, it comes from the idea that Web3, backed by the blockchain itself, allows users to interact publicly or privately without needing a “trusted” third party.
Permissionless simply means that anyone, both users and suppliers, can participate without permission from any local or otherwise governing body.
How to Access Web3
Accessing Web3 is simple, all you need is the proper Web3 wallet which you will use as your digital signature. You can access Web3 by using a Web3 wallet such as Metamask, which acts as your digital signature and verification when exploring different variations of the decentralized web.
Once you download your Web3 wallet, you can begin exploring Web3 by using the browser in your Metamask app. Simply sign in to Metamask, go to Browser, and then enter the Web3 site that you wish to visit. Once you land on the site, you will sign in using your wallet signature.
Keep in mind that it took over ten years to transition from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0, and it is expected to take just as long, if not longer, to fully implement Web 3.0. However, the technologies that some people believe are going to make up and ultimately define Web 3.0 are currently being developed, and many of them are used already.
Characteristics of Web3
Characteristics of Web3 are constructed with artificial intelligence (AI), semantic web, and ubiquitous computing properties. The idea behind using AI comes from the goal of providing faster, more relevant data to end-users.
The semantic web as a concept is to categorize and store information in a way that helps teach a system what specific data means. In other words, a website should be able to understand words put in search queries the same way a human would, enabling it to generate and share better content.
While ubiquitous computing refers to embedded processing in everyday objects, which enables the intercommunication of devices in a user’s environment. This means your devices can create an ecosystem and share data to improve your experience.
The technologies which will make up these properties include microformats, data mining, natural language search, and machine learning. Web 3.0 will also be more focused on peer-to-peer (P2P) technologies such as blockchain. Other technologies such as open APIs, data formats, and open-source software may also be used while developing Web 3.0 applications.
Examples of Web3
Some examples of Web3 applications include Opensea (the largest NFT marketplace), Decentraland (an immersive virtual world), as well as Apple’s Siri and Alexa, which combine artificial intelligence and voice recognition.
These examples of Web3 applications are called Decentralized applications (dApps) and they are being used in various areas from ride sharing to online shopping, news, music, real estate, energy trading, and many other platforms.
The transition from traditional Web2 apps has already started with Web 3.0 dApps. The transition is inevitable, and it is only a matter of time before the mass adoption of these apps will take place.
We can categorize dApps into a few categories: Social networks, messaging, exchange services, cloud storage, insurance and banking, video and music streaming, and browsing.
Web 3.0 will completely change the social network game. With the use of blockchain, it will no longer be possible for social platforms to limit their users in any way. Anyone can join despite their geographical limitations.
Messaging has been an essential part of our daily lives ever since the day we started using the internet. But governments and centralized messaging services tend to store and use private messages to serve their affairs, and that is only possible because of centralization.
The solution to this is Web 3.0-powered dApps such as e-Chat, ySign, Obsidian, Riot, and so on. All of these take advantage of blockchain technology and ensure that the privacy of users is maintained using end-to-end encryption of messages. Also, since no central servers exist, there is no way to store user data.
Data storage is a field that benefits from a lot of innovation. However, the current state of data storage can be improved further with Web 3.0 technologies such as blockchain. As a normal user, you store data on Google Drive and other cloud storage solutions on the internet.
It is an entirely different story for the companies as they prefer a more robust and centralized solution to store their valuable data. The basic idea behind decentralized storage is all about sharing files and data through a peer-to-peer connection.
The security in decentralized storage is also top-notch as the sender can simply encrypt the files and then send them to the receiver. It can also break the files into pieces and then send them. Some examples of this are Filecoin and Sia.
Video and music streaming is a giant industry, with the biggest player for over a decade being YouTube. And even though they provide a great user experience, the whole concept of monopoly is not good for the industry in the long run. Things like unclear policies and content creators’ mistreatment plague the current streaming scene.
They also utilize user data for advertising purposes, which encroaches on users’ privacy. All the streaming platforms are almost free regarding cost. In that case, your data becomes the product. In Web 3.0, some streaming dApps include the likes of Livepeer, Viuly, Flixxo, and Videocoin just to name a few. All of these platforms are promising and solve the problem of video and music streaming in their own decentralized way.
Browsers are the gatekeepers of the internet, meaning they hold so much power. To browse on Web 3.0, you need a browser that fits the decentralization aspects. It also needs compatibility with dApps and blockchain-based domains.
In addition to that, browsers should be more secure and have the protection of their users as a top priority. Two of the best Web 3.0 browsers are Brave and Breaker browsers.
Final thoughts on Web3
Web 3.0 is the next natural step in the evolution of the internet that gives the power back to the users as opposed to large corporations. By leveraging the trust and transparency of blockchain technology, users of Web3 can expect an overall safe and immersive experience.
Furthermore, Web3 is the foundation for many other technologies that will play a greater role in the development of how we use the internet. Some of these things include digital ownership through NFTs and smart contract technologies, as well as fully-immersive virtual worlds where we can all interact with one another, from anywhere in the world.
Only time will tell what the future of Web3 really holds, but whatever it is, we can assure that the users will ultimately hold the power, and large corporations will be at the mercy of their users’.

6 thoughts on “What is Web3? (Here’s A Simple Explanation)”
Comments are closed.